By Sarah Burns, Coordinator, Global Partnership for Sustainable Development Data
The speed with which the deadly coronavirus can spread has enabled it to transform from one isolated case to over 23 million cases worldwide in a matter of months (and rising). Now, the near ubiquitous nature of the virus has created immense challenges for governments as they quickly devise prevention and response plans. Effectively fighting the COVID-19 pandemic requires extensive coordination, planning, and resources — adequate testing, movement restrictions, sufficient hospital capacity, robust health care staffing, and personal protective equipment, to name a few. But it also requires government decision-making at a pace we’ve rarely seen. Ensuring critical interventions are as effective as possible demands good data, and the ability to analyze and understand the data.
How many new cases are there each day? Where are cases concentrated? How many people have been tested? Who is most vulnerable? Answers to these questions permit an informed, direct, and timely response. Moreover, understanding and quantifying the various dimensions of COVID-19’s impact on all sectors will help governments around the world protect people. This, however, will require timely and quality data to inform mitigation plans and post-COVID-19 recovery.
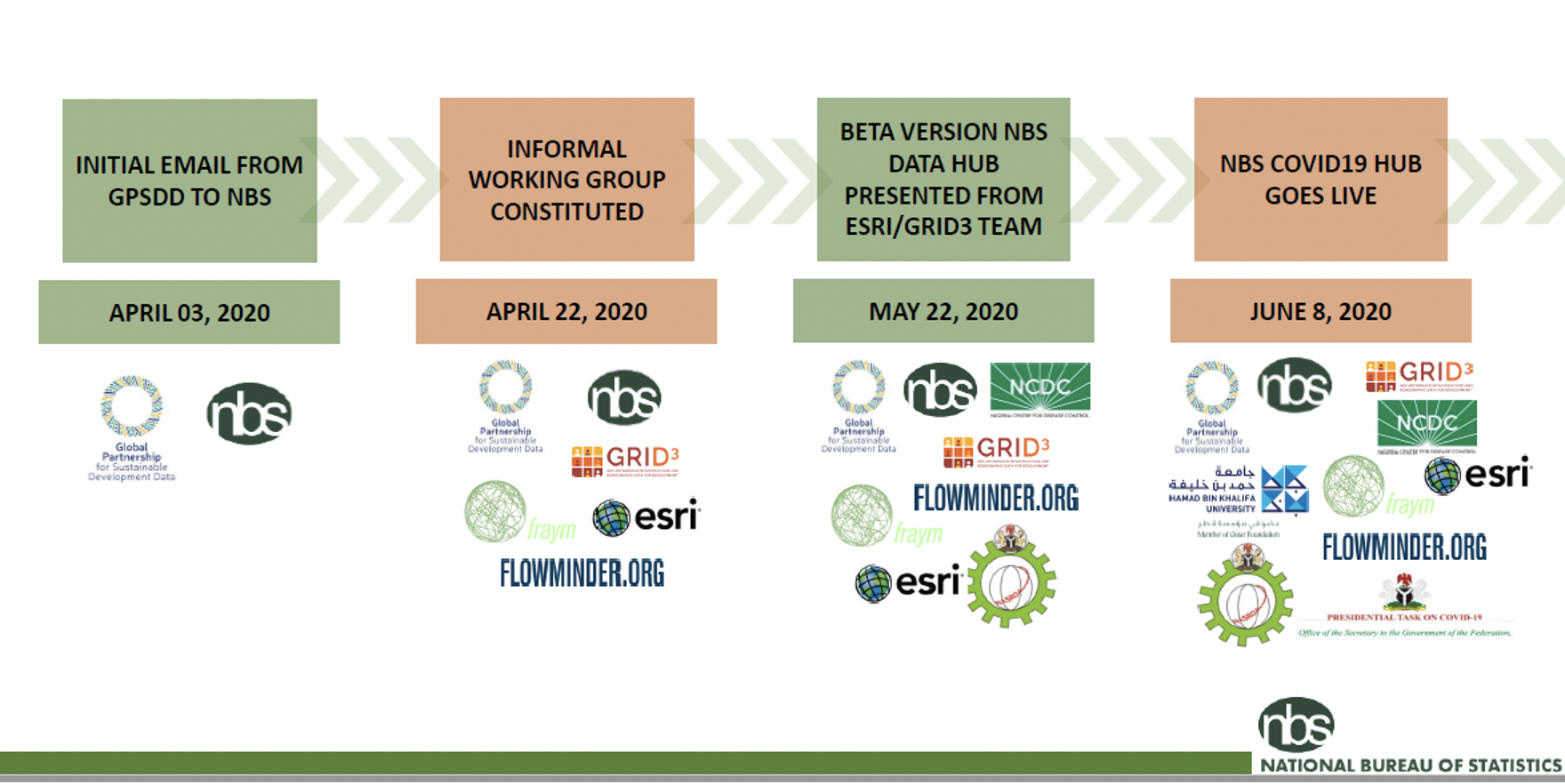
Nigeria’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) well understood this urgent need for data. In early April 2020, NBS attended the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development Data’s (the Global Partnership) cross-country virtual peer exchange on COVID-19 response. In that meeting, NBS learned about COVID-19: Data for a resilient Africa, a regional initiative that aims to deliver the required data and tools at scale and develop the data infrastructure to support decision-making for effective COVID-19 response. The Global Partnership and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa launched this initiative, bringing together their large networks, partnership brokering experience, technical capacity building, and political know-how to mobilize relationships and resources for public health, social protection, and economic recovery.
Dr. Yemi Kale, the Statistician-General of Nigeria, immediately recognized how this program could strengthen his country’s COVID-19 response. Less than 10 days later, NBS, the Global Partnership and representatives from GRID3, ESRI, Flowminder, and Fraym convened to establish an informal working group with the aim of creating a COVID-19 data hub for Nigeria – a data infrastructure that would bring together relevant data in a succinct format and boost Nigeria’s already-established National COVID-19 Multi-Sectoral Pandemic Response Plan.
On 8 June 2020, the COVID-19 data dashboard was launched on the National Bureau of Statistics website (https://nigeria-coronavirus-response-data-hub-nbs-nigeria.hub.arcgis.com/). By pulling together a wide array of COVID-19 data, the hub combines and centralizes data and visualizations from government agencies, providing decision-makers and the general public with a go-to source for COVID-19-relevant population data. There is a vast amount of critical information within the hub, including locations of health care facilities, cases by region, and locations of infection epicenters, coming from diverse sources such as GRID3, Qatar Computing Research Institute, Our World in Data, and the MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis at Imperial College.
“Initiating engagement, facilitating and engaging collaboration between partners and governmental agencies…[the Global Partnership] gave us an opportunity to achieve our goals regarding COVID-19 data with guidance and support from global experts,” says Lola Talabi-Oni, Technical Adviser from the Office of the Statistician-General.
NBS is routinely asked to provide timely and reliable data and analysis to support policy-makers at all levels. The data hub has allowed NBS to use visualization to better analyze data. Ms. Talabi says that “this has been the biggest benefit from the data hub partnership — capacity building towards data visualization. Without this critical skill, we would have likely made raw data available on the NBS website.”
The partnership brought together multiple organizations working with Nigeria’s COVID-19 data and data visualization expertise to produce a data hub that is accessible and easily digestible for policymakers and the general public. The information can then be used to aid decisions about intra- and inter-regional vulnerabilities, improving access to healthcare and testing, planning around lockdowns, and socio-economic support for communities most affected by the pandemic.
As a direct result of this partnership and data hub, the Presidential Task Force, the highest decision-making body in relation to coronavirus response, is working with NBS to build a database for internal use that will help guide their decisions. In addition, NBS has also been approached by civil society organizations who are interested in incorporating data about the impact of coronavirus on child labor practices, highlighting a gap in the measurement of the pandemic's impact on vulnerable populations.
With a virus that has spread so rapidly, timeliness is key. The Global Partnership wasted no time and was able to quickly connect the Nigerian government and statistical office with partners from the private sector and civil society, who provided the resources necessary to rapidly create a tool that will guide policy throughout the fight against COVID-19.